New in BCC10
Overview
BCC Cross Glitch is an auto-animating transition effect for simulating some of the kinds of errors and artifacts that can be apparent during digital video playback. It is useful as a style element on video or titles to create a sense of energy and movement. It makes use of auto-animation so it requires little or no keyframing. BCC Cross Glitch allows a single glitch to last for more than one frame with controls over how that glitch grows and fades over its lifetime, thus allowing more dynamic and realistic glitch behavior that can be achieved with glitches that last only a single frame. Note that for the purposes of this document, a single “glitch” is defined as an individual period of time during which the errors and artifacts appear. A special Curves preview mode allows visualizing the relative locations of the glitches over time.
Parameter Controls
Presets and Common Controls
BCC filters come with a library of factory installed presets plus the ability to create your own custom presets and preview them with the BCC FX Browser™.
BCC filters also include common controls that configure global effect preferences and other host-specific effect settings.
For more information about working with presets and other common controls, Click Here.
Layer to Reveal: This layer selection popup is not relevant when you have applied the filter as a true NLE-style transition and it will be hidden or disabled in that context. When applied as a normal “effect” as opposed to a transition, however, this menu is used to select the “Incoming” or “Reveal” layer for the transition.
Animation: Menu controlling what drives the animation of the transition.
- Auto – automatically generates a transition based on the transition length (when used as a transition) or the clip length (when used as a filter).
- Percent Done – requires the user to set keyframes to control the transition progression. Can be useful in customizing the exact timing of the transition or when applying the filter as a stylized effect as opposed to a direct NLE-style transition.
Percent Done: Disabled/Hidden by default. When the Animation menu is changed to Percent Done then this slider can be manually keyframed to control the transition progression.
Trigger Mode: Offers 2 basic modes for how / when glitches are triggered in the effect.
- Automatic: the time at which glitches are triggered is based only on the values of the Glitch Interval and Interval Randomness parameters.
- Intensity Threshold: a single glitch is triggered whenever the Glitch Intensity crosses a specified threshold (Trigger Threshold parameter) in a positive direction (from lower to higher value) either by animating Glitch Intensity by keyframing or by driving Glitch Intensity through the Beat Reactor.
Glitch Intensity: Global Intensity control that applies to all Video Glitch groups.
Intensity Randomness: Randomizes the global glitch intensity.
Intensity Seed: Allows for changing the randomized intensity of glitches.
Intensity Trigger Threshold: With Trigger Mode set to Intensity Threshold, this threshold is the Glitch Intensity value at which a glitch will be triggered as Glitch Intensity increases.
Glitch Interval: Global interval control that applies to all Video Glitch groups. Expressed in the number of frames between glitches.
Interval Randomness: Randomizes the global Glitch Interval.
Interval Seed: Allows for changing the randomized timing of all Glitches. Each individual glitch group also contains an additional seed parameter to allow varying the timing of the separate glitch elements.
Start at 0: Enabling this checkbox forces the first glitch to occur at the beginning of the effect (even when Interval is randomized).
Glitch Duration: The length of the Glitches in time. It is expressed as a percent of the Interval so the duration in terms of frames or seconds changes if the Interval is changed.
Duration Randomness: Randomizes the Glitch Duration.
Duration Mode:
- Actual:
- Average:
Edge Handling: The Shift and Shake features described below can create instances where the image is offset so there are areas along the edges of the frame where no image appears during Glitches. Edge Handling offers options to Tile or Reflect the image to fill those areas.
Note – Each individual group below includes its own Interval Seed, and varying those seeds between groups allows for varying the timing between the different Glitch components.
Block Damage Group
With Block Damage enabled, a field of square blocks overlays the image during a glitch. By design, in a typical effect using Block Damage some blocks will be more apparent than others depending on how they composite with the underlying image in that area of the frame, as seen on the left hand image below. When the same Block Damage pattern is applied to a solid color so all the blocks are clearly defined at once, as in the right hand image below, the darker more saturated areas of squares are what is meant by Blocks, and the striped or weaved designs which can be seen within some Blocks are what is referred to in the parameter descriptions below as Patterns.
Enable Block Damage: Controls whether the Block Damage elements are enabled or disabled.
Block Damage Intensity: Used to adjust the overall amount of blocks on screen during a glitch.
Peak Position: Defines at what point within the duration of the glitch shows the most blocks, with zero being the beginning of the glitch, 100 the end, and 50 the midpoint.
Minimum Intensity: Allows for forcing a minimum amount of blocks for the glitch duration.
Intensity Randomness: Adds more variability to the animation within the glitch duration – larger values give a more flickering appearance.
Block Run Length: Controls the number of blocks between gaps. A value of zero generates completely independent blocks. A value of 100 generates one run of blocks with gaps on either side.
Block Size: Offers 5 options for the size of the Blocks.
Block Saturation: Values > 100 oversaturate and values < 100 desaturate the Block Damage area.
Block Blend Mode: Blend options for compositing with source image. Depending on the Blend Mode, the image freeze and Pattern effects can be more or less apparent.
Pattern Amount: Increases or decreases the percentage of the Blocks displaying a Pattern.
Pattern Complexity: Adds a variety of smaller patterns within the blocks with patterns.
Pattern Opacity: Sets the maximum opacity for the Patterns.
Vary Pattern Opacity: Randomly reduces max opacity for some Patterns by varying amounts.
Vary Pattern Color: Tints some percentage of the patterns with colors. A value of zero leaves them all black.
Freeze Source: When enabled, the area of the source video within the block damage freezes and holds on the same frame for the duration of the glitch.
Block Seed: Allows for changing the randomized arrangement of the Block Damage.
Block Interval Seed: Allows for changing the randomized timing of Block Damage.
Shift Group
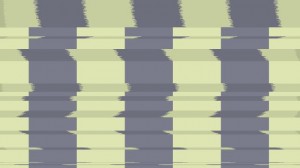
With Shift enabled, horizontal bands of the image become horizontally displaced and skewed during a Glitch. As a primarily horizontal distortion, it stands out more in areas of the image with more high contrast vertical edges. When using multiple groups the order of processing relative to parameter group layout is top to bottom so when using Block Damage the Blocks are affected by Shift.
Enable Shift: Controls whether the Shift distortions are enabled or disabled.
Shift Group Intensity: Used to adjust the overall strength of the shift distortions during a glitch.
Peak Position: Defines at what point within the duration of the glitch shows the most shift, with zero being the beginning of the glitch, 100 the end, and 50 the midpoint.
Minimum Intensity: Allows for forcing a minimum intensity of shift for the glitch duration.
Intensity Randomness: Adds more variability to the animation within the glitch duration – larger values give a more flickering appearance.
Line Duplication: Artifacts where horizontal lines of pixels are duplicated and positioned adjacent to each other vertically. This creates the appearance of vertical stripes in areas of the image.
Shift Amount: Increases or decreases the peak horizontal Shift and Jitter amount in the shift animation that occurs over the duration of the Glitch.
Shift Density: Used to adjust the overall density of Shift bands on screen during a Glitch.
Shift Run Length: Controls the number of shifted lines between gaps.
Skew: Defines the peak horizontal Skew amount in the shift animation that occurs over the duration of the Glitch.
Jitter: Jitter adds an additional randomized horizontal shift to each line (1 pixel horizontal band) within the Shift band.
Line Drop: Line Drop fades the opacity of every other line (every other 1 pixel horizontal band).
Line Drop Density: Allows for randomly skipping some line drops (when value is < zero).
Intensity Seed: Allows for changing the randomization of Shift Intensity.
Shift Interval Seed: Allows for changing the randomized timing of Block Damage.
Shake Group
With Shake enabled, the image position is offset and/or skewed / rotated over the duration of the Glitch. Any Block Damage or Shift elements are offset by effects in the Shake group.
Enable Shake: Controls whether the Shake distortions are enabled or disabled.
Intensity: Scales the Intensity of all the attributes of the Shake group.
Peak Position: Defines at what point within the duration of the glitch shows the most shake, with zero being the beginning of the glitch, 100 the end, and 50 the midpoint.
Minimum Intensity: Allows for forcing a minimum intensity of shake for the glitch duration.
Intensity Randomness: Adds more variability to the animation within the glitch duration – larger values give a more flickering appearance.
Shake Amount: Controls amount of overall position offset (also scales RGB Split value).
Shake X: Horizontal position offset.
Shake Y: Vertical position offset.
RGB Split: Controls how much RGB are offset from each other in the direction of Shake movement.
Skew: Horizontal skew applied to the image.
Rotate: Rotation anchored to the center of the image applied to the image.
Shake Intensity Seed: Allows for changing the randomization of Shake Intensity.
Shake Interval Seed: Allows for changing the randomized timing of Shake effects.
Flicker Group
With Flicker enabled, the brightness and/or saturation of the image can flicker during Glitches.
Enable Flicker: Controls whether the Flicker distortions are enabled or disabled.
Flicker Group Intensity: Scales the Intensity of all the attributes of the Flicker group.
Peak Position: Defines at what point within the duration of the glitch shows the most flicker, with zero being the beginning of the glitch, 100 the end, and 50 the midpoint.
Minimum Intensity: Allows for forcing a minimum intensity of flicker for the glitch duration.
Intensity Randomness: Adds more variability to the animation within the glitch duration – larger values give a more flickering appearance.
Brightness: Controls the peak level of the brightness effect on the image.
Brightness Randomness: Controls the randomness of the brightness distortion.
Brightness Offset: Allows for setting it to flicker more brighter or darker than the original. A value of Zero flickers brighter and darker, a value of 100 flickers only brighter, a value of negative 100 flickers only darker.
Flicker Saturation: Controls the extremity of the saturation effect on the image.
Saturation Randomness: Controls the randomness of the saturation distortion.
Saturation Offset: Allows for setting it to flicker more oversaturated or desaturated. A value of Zero flickers both ways, a value of 100 flickers only oversaturated, a value of negative 100 flickers only desaturated.
Flicker Intensity Seed: Allows for changing the randomization of Flicker Intensity.
Flicker Interval Seed: Allows for changing the randomized timing of Flicker effects.
Use Background Color: Enabled so a color not transparency will fill the areas created by Shake, Shift, and Line Drop.
Background Color: The color used to fill background areas described above.
Animation Tuning Group
These parameters control the overall timing of the transition. On hosts which permit on-screen heads up display widgets (such as AE, Premiere, and Avid), you should never need to modify these sliders directly since they can be configured in a more convenient and intuitive manner by manipulating the widgets directly in your comp/preview pane. On hosts without heads up display widgets you can use these sliders directly to fine tune your animation timing, taking advantage of the View Ease Curve option to help visualize the animation rates.
Ease In: Controls how quickly or slowly the glitch intensity increases at the beginning of the transition.
Ease Mid: Controls the rate of change of the glitch intensity (how quickly it reaches its peak amount and how long it holds there) during the middle of the transition.
Ease Out: Controls how quickly or slowly the glitch intensity decreases at the end of the transition.
Dissolve Duration: Controls the timing of the underlying dissolve relative to the timing of the rest of the transition.
View Ease Curve: (Only visible/enabled in hosts that don’t support heads up display widgets for manipulating these controls directly on screen.) Enable this control to display a preview graph of the the animation curves rendered into in the composite window.