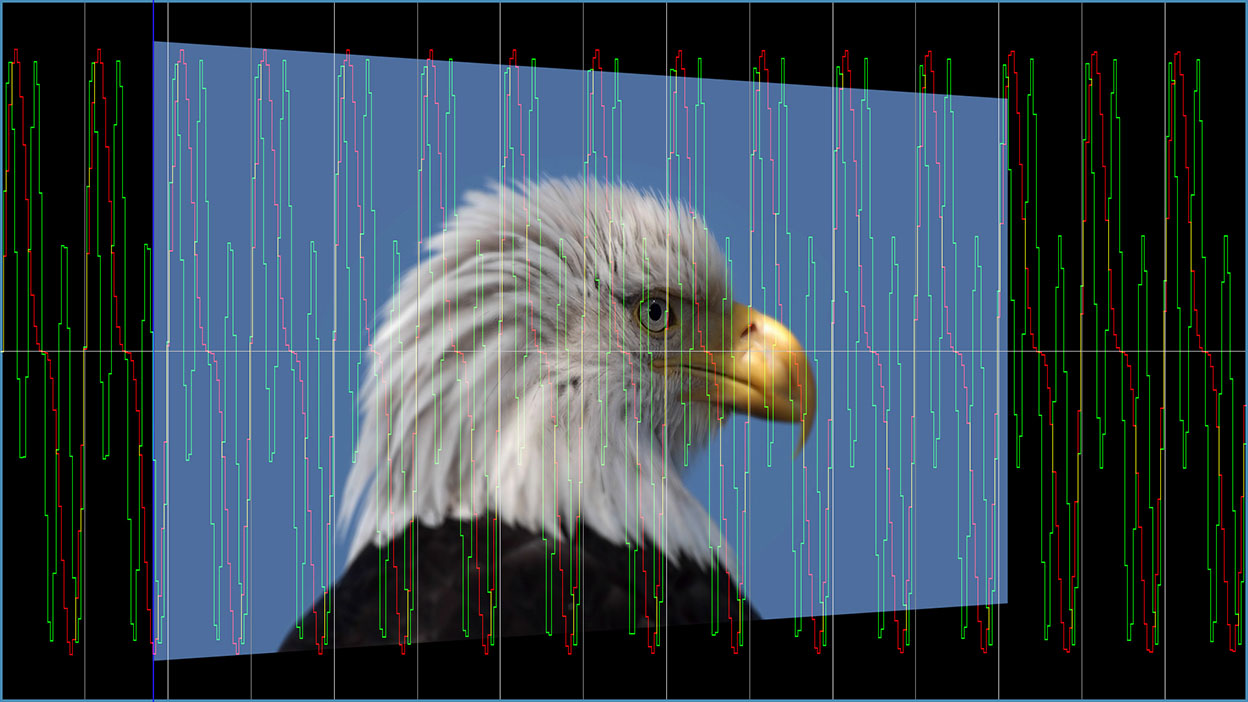
Overview
Jitter allows you to vary one or more attributes of a source layer over time, such as size, position, opacity, brightness, or contrast. Additional controls choose the type of variance used for the jittering and allow you to view color-coded graphs of the jittered parameter values.
Boris Continuum Complete includes both a BCC Jitter and BCC Jitter Basic. The two filters are very similar except that BCC Jitter Basic does not include all the parameters; BCC Jitter provides more options for controlling the effect; while BCC Jitter Basic is streamlined for when you want to create a simple Jitter effect.
Function
The Jitter filter has four basic groups of controls that are used to jitter attributes of the source layer. The following steps outline the recommended usage of this filter.
1. Apply the BCC Jitter or BCC Jitter Basic filter the clip you want to Jitter. Set the Source menu set to the Filtered Layer. The Default setting of None uses the layer the filter is applied to.
2. Use the Jitter 1, 2, and 3 parameters to create up to three different jitter curves (BCC Jitter Basic allows you to create one jitter curve). The curves represent the variation of a parameter value over time. View the Jitter Curves by setting the Curve View menu while you adjust the Jitter parameters to see the affects your adjustments have on the parameters.
3. Apply each Jitter curve to up to three parameters using the Destination 1, 2, and 3 controls. For example, you could use the same variance pattern to affect the source image’s scale, opacity, and contrast.
4. Adjust the impact of each Jitter curve on the destination parameter using the Amount 1, 2, and 3 controls. Amount affects the intensity, rather than the shape, of the applied Jitter curve.
- Note: The Jitter filter includes extensive parameters for you to customize. You may want to start by using a preset to help you become familiar with the parameters.
Presets and Common Controls
BCC filters come with a library of factory installed presets plus the ability to create your own custom presets and preview them with the BCC FX Browser™.
BCC filters also include common controls that configure global effect preferences and other host-specific effect settings.
For more information about working with presets and other common controls, Click Here.
Curves Parameter Group
The parameters in this section allow you to view the Jitter curves as you make adjustments to them. These curves plot the values of the jittered parameter over time.
The Curve View menu displays a graph of the effect of the jitter over time. If one of the Jitter Shape controls is Off, that jitter is inactive and its curve does not appear on the graph. This menu setting determines how the jitter curves are represented on the graph. When you use the Draft Only options, the curves are not visible in the rendered effect. However, you must preview in Draft mode in your host for these options to display. When you use the Renderoptions, the curves appear in the rendered effect.
- Off does not display any jitter curves.
- Curves: Draft Only and Curves: Render display curves showing the amount of jitter at each frame or at selected frames of the effect.
- Curves Over Layer: Draft Only and Curves Over Layer: Render display the jitter curves over the rendered clip. This mode allows you to simultaneously preview the jitter curves and the rendered output, which can be useful for adjusting the effect.
- Curves Over Comp: Draft Only and Curves Over Comp: Render display the jitter curves over all other layers in the effect.
The vertical axis on the graph represents the current time in the effect. The horizontal axis represents the base parameter value (set by the Source or Insert parameter values) before it is jittered. The red curve represents Jitter 1, the green curve represents Jitter 2, and the blue curve represents Jitter 3.
 |
The Curve View menu determines how the jitter curves are represented on the graph.
- Curves displays the amount of jitter at each frame or at selected frames of the effect.
- Curves Over Layer displays the jitter curves over the rendered clip layer. This mode allows you to simultaneously preview the jitter curves and the rendered output, which can be useful for making adjustments to the effect.
- Curves Over Comp displays the jitter curves over all other layers in the effect.
Curves Parameter Group
The Time View menu controls the time range shown on the graph. Full Effect displays the jitter curves from the start to the end of the effect. 16, 8, 4, and 2 display the curves for the given number of seconds after the frame specified by Scroll Curves.
Scroll Curves selects the first frame in the effect that is displayed when Time View is set to 16, 8, 4, or 2. This parameter has no effect if Time View is set to Full Effect.
The Source menu sets the layer in the timeline used to create the effect.
Geometry Parameter Group
The Geometry parameters adjust the source layer’s position, size, rotation, and opacity.
Lock to Scale X checkbox locks the Scale Y to the Scale X value, preserving the aspect ratio of the source image as scale adjustments are made. Deselect Lock to Scale X to adjust Scale X and Y independently.
Scale X sets the horizontal scale of the source layer. The Scale X value is expressed as a percentage of the source layer’s original width.
Scale Y sets the vertical scale of the source layer. The Scale Y value is expressed as a percentage of the source layer’s original height.
Position X and Y sets the horizontal and vertical position of the source layer.
Position Z sets the apparent depth of the source layer. Increasing positive values move the source further away from the viewer, and decreasing negative values draw the source closer to the viewer.
Tumble, Spin, and Rotate move the source layer around the X, Y, and Z axis respectively. Tumble, Spin, and Rotate can be animated over values greater than 360° in order to make the layer complete more than one full revolution.
When the Lock Pivot to Center checkbox is selected, the layer tumbles, spins, and rotates around its ow n center. If this option is deselected, you can set an external pivot point around which to tumble, spin, and rotate the layer., using the Pivot X, Y and Z parameters. The BCC Jitter Basic filter does not include this parameter.
Pivot X, Pivot Y and Pivot Z set the X, Y, and Z coordinates of the pivot point. If the Lock Pivot to Center checkbox is selected, moving the pivot point parameters have no affect. The BCC Jitter Basic filter does not include this parameter.
Opacity scales the opacity of the source layer. When Opacity is 0, the layer is completely transparent. As the Opacity value increases, the layer becomes increasingly opaque, and at a value of 100, the layer is completely opaque.
Motion Blur Parameter Group
Select the Motion Blur On checkbox to turn on motion blur. If Motion Blur On is not selected, the other parameters have no affect.
- Warning: Motion Blur is an especially memory-intensive feature. It is particularly useful to work in DraftMode when creating an effect with motion blur.
The Motion Blur Smoothness menu determines how many times the effect samples between the time the shutter opens and the time it closes. Increasing the number of samples creates a smoother blur but increases render and preview time proportionately. Choose Rough, Medium, Smooth, or Smoothest. Rough uses the fewest samples, while Smoothest uses the most.
Shutter Angle refers to the workings of a conventional film camera. Normally the shutter is open to 180°, meaning that the shutter is open for half of each frame. Increasing the angle opens the shutter longer, creating a wider blur. Decreasing the angle produces a thinner blur.
Selecting the Adaptive Motion Blur checkbox causes the effect to take fewer samples when the source moves more slowly. Selecting this checkbox usually does not have a visible effect, but improves rendering speed.
The Shape Jitter 1 menu sets the shape of the Jitter curve. The best way to understand how these shapes affect the jittered parameters is to select a setting in the Curve View menu to view Jitter Curves and see the shape of the curve over time. The curves can be modified using the Jitter Frequency, Jitter Smoothness, Jitter Frequency, Jitter Random Seed and/or Master Jitter 1 settings. Hosts that do not support contextual controls (such as Final Cut Pro) use the Timing Jitter 1 and Master Jitter 1 parameters.
- Off turns Jitter 1 off. If shape Jitter 1 is set to Off, the other Jitter 1 parameters have no effect.
 |
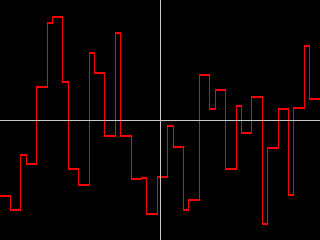
- Noise Jumps causes the noise to jump to a new value in increments set by the Jitter 1 Separation and Jitter 1 Random Seed settings. Hosts that do not support contextual controls use the Timing Jitter 1 setting.
 |
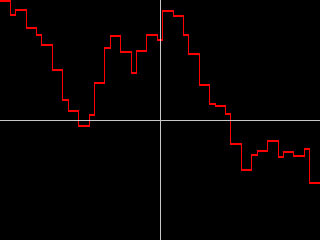
- Random Walk causes the noise to start at 0, then add a new random number in increments set by the Jitter 1 Separation and Jitter 1 Random Seed settings. Hosts that do not support contextual controls use the Timing Jitter 1 setting.
 |
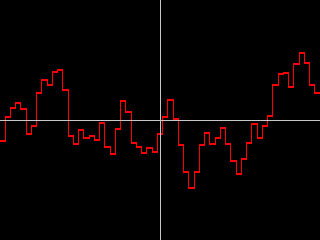
- Smooth Noise creates a new noise value every frame, then smooths the curve that is created. Jitter 1 Smoothness and Jitter 1 Random Seed adjust the width of the curve smoothness. Hosts that do not support contextual controls use the Timing Jitter 1 setting.
 |
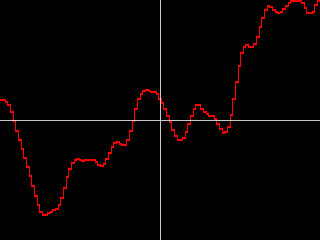
- Smooth Walk creates a Random Walk curve, then smooths the result. Jitter 1 Smoothness and Jitter 1 Random Seed adjust the width of the curve smoothness. Hosts that do not support contextual controls use the Timing Jitter 1 setting.
 |
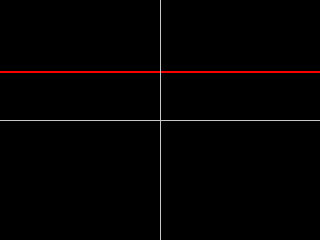
- Constant adds the Master Jitter 1 value to the base parameter value set by the Source and Insert settings, creating a static effect.
 |
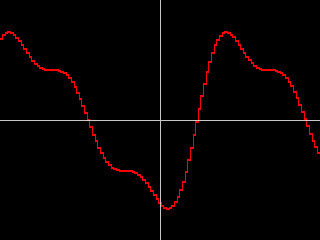
- The remaining choices all produce regular waves of varying shapes. Most of these choices have fairly descriptive names. The Spectrum choices are all variations on the sine wave (the curve at right is an example of a Spectrum wave). For each of these choices, Jitter 1 Frequency or Timing Jitter 1 adjust the frequency of the wave, and Master Jitter 1 adjusts the amplitude (height) of the wave.
 |
Jitter 1, 2, and 3 Parameter Groups
The Jitter 1, 2, and 3 parameter groups create three different jitter curves, each of which can apply to up to three parameters. Jitter 2 and Jitter 3 parameters function similarly to Jitter 1 parameters, which are described in this section.
- Note: The only difference between the three Jitter parameters sections is that each Jitter can apply to Jitter parameters below it. That is, Jitter 3 can apply to Jitters 1 and 2, Jitter 2 can apply to Jitter 1, and Jitter 1 cannot be applied to other Jitters.
- Warning: The BCC Jitter Basic filter only allows you to apply one Jitter curve.
Jitter 1 Master adjusts the intensity of the jitter by scaling all of the other jitter parameters. For this reason, each Shape Jitter 1 curve responds slightly differently to Master Jitter 1. When Master Jitter 1 is 0, no jitter is created.
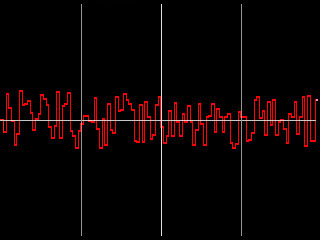 |
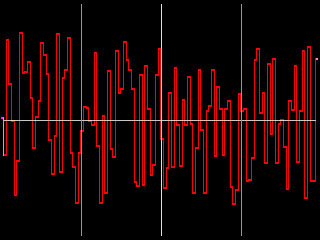 |
| Master Jitter 1=25 | Master Jitter 1=75 |
The effect of Timing 1 Jitter depends on which shape is selected in the Shape Jitter menu. See the Shape Jitter menu for details. The Timing Jitter parameter only displays in hosts that do not support contextual controls, such as Final Cut Pro.
The effect of Jitter Smoothness and Jitter Separation depend on which shape is selected in the Shape Jitter menu. See the Shape Jitter menu for details. Jitter Smoothness and Jitter Separation only appear in hosts that support contextual controls.
Jitter 1 Random Seed sets the value that is input to the random number generator used to generate noise. Adjust this value when you like the overall effect but want to adjust the random configuration of the jitter curve.
The effect of Jitter Frequency depend on which shape is selected in the Shape Jitter menu. See the Shape Jitter menu for details. Jitter Smoothness and Jitter Separation only appear in hosts that support contextual controls.
Jitter 1 Offset offsets the position of the jitter curve by the specified number of frames. Adjusting this value controls which point on the curve corresponds to a given frame.
The Jitter 1 Destination 1 menu selects which parameter is affected by the jitter. Jitter 1 Destination 2 and Jitter 1 Destination 3 allow you to choose two more parameters to jitter.
- When Destination is set to Off, no parameters are affected.
- Scale jitters both the X and Y Scale.
- Motion jitters the motion of the layer in the X, Y, and Z directions simultaneously. If Motion is selected, the Jitter Amount is proportionate to the layer’s speed, so when the layer is still, no jitter is applied.
- XY Wobble jitters the layer in the direction perpendicular to the layer’s direction of motion in the X and Y planes. For example, if the layer is moving horizontally, XY Wobble jitters the layer vertically. If XY Wobble is selected, the Jitter Amount is proportionate to the layer’s speed, so when the layer is still, no jitter is applied.
- Angular Motion jitters Tumble, Spin, and Rotate in amounts proportionate to each parameters rate of change. When Tumble, Spin, or Rotate is constant, the parameter is not affected by the jitter.
- Insert 1 Red, Insert 1 Green, and Insert 1 Blue affect the respective color channel in the chosen Insert 1 Color. The Insert 2 and Insert 3 Red, Green, and Blue choices function in the same way but affect the Insert 2 and Insert 3 Colors, respectively.
- The remaining choices affect the parameters of the same name.
Insert 1, 2, and 3 Parameter Groups
Each of these parameter groups can be used to apply a simple effect to the source image. The parameters function in the same way in each section. The Effect Insert menu determines which effect is applied. Effect are adjusted with the Amount and Parameter controls. Several effects use the Color parameter as well. The controls behave differently depending on which the selected effect.
- Off applies no additional effect to the source layer.
- Bright-Contrast adjusts the brightness and contrast of the source layer. When Bright- Contrast is chosen, Amount adjusts brightness, and Parameter adjusts contrast.
- Hue-Sat adjusts the hue and saturation of the source layer. Amount adjusts the hue angle, and Parameter adjusts the saturation.
- Black & White mixes the source image with a black and white copy of itself. Amount controls the mixture of the images. Increasing Amount values replace the colored image with the black and white copy, and at a value of 100, the image is completely black and white. Negative Amount values have no affect. Parameter has no affect when Black & White is chosen.
- Black & Color mixes the source image with a copy of itself that is tinted black and the chosen Color. Amount controls the mixture of the images. Increasing Amount values replace the original source image with the tinted copy, and at a value of 100, the source is completely tinted. Negative Amount values have no affect. Parameter has no affect when Black & Color is chosen.
- Color & White mixes the source image with a copy of itself that is tinted the chosen Color and white. Amount controls the mixture of the images. Increasing Amount values replace the original source image with the tinted copy, and at a value of 100, the source is completely tinted. Negative Amount values have no affect. Parameter has no affect when Color & White is chosen.
- Colorize mixes the source image with the chosen Color. Amount controls the mixture of the source and color. Increasing Amount values replace the original source image with the color; at a value of 100, the source is entirely replaced by the color. Negative Amount values have no affect. Parameter has no affect when Colorize is chosen.
- Blur applies a blur to the source image. Amount controls the amount of blur. Negative Amount values have no affect. Parameter controls the amount of blur in each direction. Increasing positive Parameter values increase the horizontal blur, while decreasing negative values increase the vertical blur. When Parameter is 0, the image blurs equally in both directions.
- Choke shrinks or expands the opaque areas in the source image’s alpha channel. Increasing positive Amount values increase the size of the opaque regions, while decreasing negative values decrease the size of the opaque regions. When Choke is chosen, Parameter has no affect.
- Radial Wipe creates a wipe effect which keys out a portion of the source image. The image keys outside of a circle whose diameter is controlled by the Amount. When Amount is 0, the image is unchanged. Increasing this value decreases the diameter of the circular opaque region, removing more of the image. At a value of 100, the entire source keys out. Negative Amount values have no affect. Parameter adjusts the softness of the edges of the opaque region. When Parameter is 0, the edges are completely hard. Increasing this value increasingly blends the edges with the background. Negative Parameter values have no affect.
- Key Out Dark keys out the darker pixels in the source image, making them transparent. Amount controls the value of the key threshold. Increasing this value raises the threshold, increasing the range of luminosities that key out. Increasing Parameter increases the softness of the edges of the opaque regions in the image. Negative Parameter values have no affect.
- Key Out Light keys out the lighter pixels in the source image, making them transparent. Amount controls the value of the key threshold. Increasing this value lowers the threshold, increasing the range of luminosities that key out. Increasing Parameter increases the softness of the edges of the opaque regions in the image. Negative Parameter values have no affect.
- Key Out Color keys out pixels whose channel values are similar to the chosen Color. Amount controls the width of the range of similar values that key out. As Amount increases, a wider range of colors similar to the Color key out. Increasing Parameter increases the softness of the edges of the opaque regions in the image. Negative Parameter values have no affect.
- Key In Color keys out pixels whose channel values are dissimilar to the chosen Color. Amount controls the width of the range of dissimilar values that key out. As Amount increases, a wider range of colors dissimilar to the Color key out. Increasing Parameter increases the softness of the edges of the opaque regions. Negative Parameter values have no affect.