 |
|
| Source image | Filtered image |
Overview
Mosaic allows you to pixelate images to achieve a range of mosaic effects using a few simple parameters and a PixelChooser.
Function
Presets and Common Controls
BCC filters come with a library of factory installed presets plus the ability to create your own custom presets and preview them with the BCC FX Browser™.
BCC filters also include common controls that configure global effect preferences and other host-specific effect settings.
For more information about working with presets and other common controls, Click Here.
Compare Mode
The BCC Compare Mode provides a convenient mechanism to compare the effect result with the original source layer. It provides several variations on basic split-screen views with the filtered clip placed next to the unedited original.
For more information on the Compare Mode, Click Here.
Compare Mode pop-up: Controls what is displayed by the Compare Mode. The options are:
- Off shows the output of the filter.
- Side By Side the left side of the output shows half of the incoming image, and the right side shows the same half of the image as processed by the filter. When in Side-by-Side mode, the corresponding Slide and Right Offset sliders become available.Wipe enables the user to interactively wipe the effect across the image. The left side of the wipe bar on the image output shows the unfiltered image, while the right side of the wipe bar shows the filtered result. When in Wipe mode, the corresponding Wipe slider becomes available.
- Wipe/Slide operates as a Wipe function when Wipe is selected in Compare Mode, and as a Slide function when Side-‐By-‐Side is selected in Compare Mode. When in Wipe mode, adjustments to this parameter moves the vertical wipe bar across the image; the region on the left of the wipe bar shows the original unfiltered image, while the region on the right shows the filtered result. When in Slide mode, adjustments to this parameter pans the image in the viewer window, maintaining the spatial relationship in the viewer between the before and after images.
- Right Offset provides a way to adjust the spatial relationship between the unfiltered original image and the filtered result in the viewer window. Adjustments to this parameter will offset the position of the filtered image in the viewer.
The Lock Pixelation checkbox locks the Pixelate Y value to the Pixelate X setting. When this option is selected, adjusting Pixelate Y has no affect. Deselect this option to adjust the Pixelate X and Y values independently.
Pixelate X and Pixelate Y set the amount of pixelation along the horizontal and vertical axis, respectively. Increasing these values reduces the number of pixels used to create the image.
When the Pixelate X and Y values are the same, the pixels forming the image have the same aspect ratio as the filtered media.
| Pixelate X & Pixelate Y=0 | Pixelate X & Pixelate Y=50 | Pixelate X & Pixelate Y=100 |
Adjusting the Pixelate X and Y values independently distorts the pixels.
| Pixelate X=0, Pixelate Y=100 | Pixelate X=50, Pixelate Y=100 |
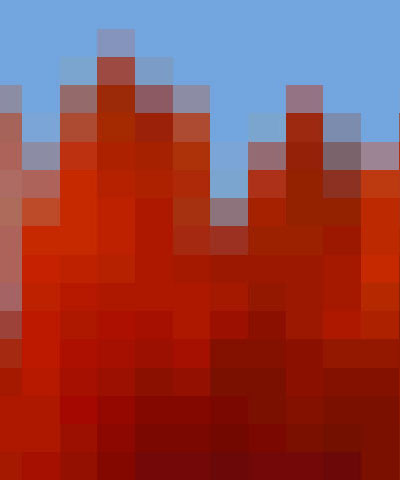
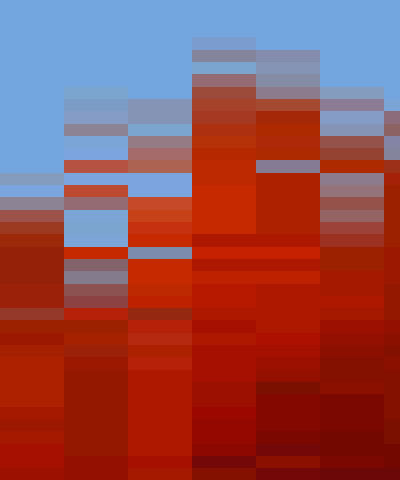
Scramble shuffles the pixels in the image. As Scramble increases, the arrangement of pixels becomes increasingly random.
 |
 |
 |
| Scramble=0 | Scramble=10 | Scramble=50 |
Scramble Seed determines which value is input to the random number generator used to scramble the pixels. Adjust this value when you like the overall effect but want to adjust the random configuration of the pixels.
The Apply Mode menu controls how the filtered image is composited with the source image. For descriptions of all the possible Apply Modes, Click Here.
Apply Mix controls the mix of the specified Apply Mode with the Normal apply mode. If the Apply Mode is Normal, Apply Mix has no affect and the parameter does not appear. If Apply Mix is 0, Apply Mode has no affect. Increase Apply Mix to blend the Apply Mode setting with the Normal apply mode.
PixelChooser
The BCC PixelChooser provides simple, built-in masking of the effect result. The PixelChooser is generally used to select a portion of the image and restrict an effect to just the selected area while maintaining the original image content in unselected regions. The selection can be based on geometric shapes or on the image’s luma/color properties.
For more information on the PixelChooser, Click Here.