Overview
BCC Organic Strands is a particle based effect used to generate 3D strands with interesting looks and convenient animation options.
Function
Presets and Common Controls
BCC filters come with a library of factory installed presets plus the ability to create your own custom presets and preview them with the BCC FX Browser™.
BCC filters also include common controls that configure global effect preferences and other host-specific effect settings.
For more information about working with presets and other common controls, Click Here.
Render
Anti-Aliasing is a smoothing process that applies to 3D and alpha edges in the effect if they appear jagged. Anti-Aliasing can slow down the responsiveness of working with the effect and so by design the plugin will not apply any Anti-Aliasing when the layer the effect is applied to is set to Draft mode. Also, using a higher AA setting will result in a somewhat slower render than using a lower AA setting so AA should only be set as high as is visually necessary to smooth the effect.
Opacity Boost can be used to uniformly adjust the overall opacity of the particles. It can be useful used in relation to other parameters creating varied opacity such as Motion Blur, Opacity Evolution, Random Opacity, etc.
Use Source As Mask will use the alpha channel of the layer to which the effect is applied to mask the output of the effect.
Use Particle Intersection allows particles to intersect with each other. This render mode can be useful for some kinds of effects but does not support particle images with transparency well.
Motion Blur offers various levels of motion blur to simulate camera shutter blur based on movement of the particles or camera
Shutter Angle determines the spread of the motion blur when it is enabled
Depth of Field Blur: determines the amount of blur in front and behind the focus of the camera.
Use Comp Camera ; When enabled, the filter will display the Cards from the perspective of the enabled AE camera whose track is topmost in the timeline. When Use Comp Camera is enabled, the Built-In Camera group is disabled.
Strands
Count determines the number of strands
Direction determines the general direction the strands extend away from the source
Spread for some Direction choices, it is possible to specify a Spread angle to control the orientation of the strands
Length determines the length of the strands, while Length Variance allows for varying the Length between strands.
Thickness determines the thickness of the strands by using larger particles to make up the strand, while Thickness Variance allows for varying the Thickness between strands.
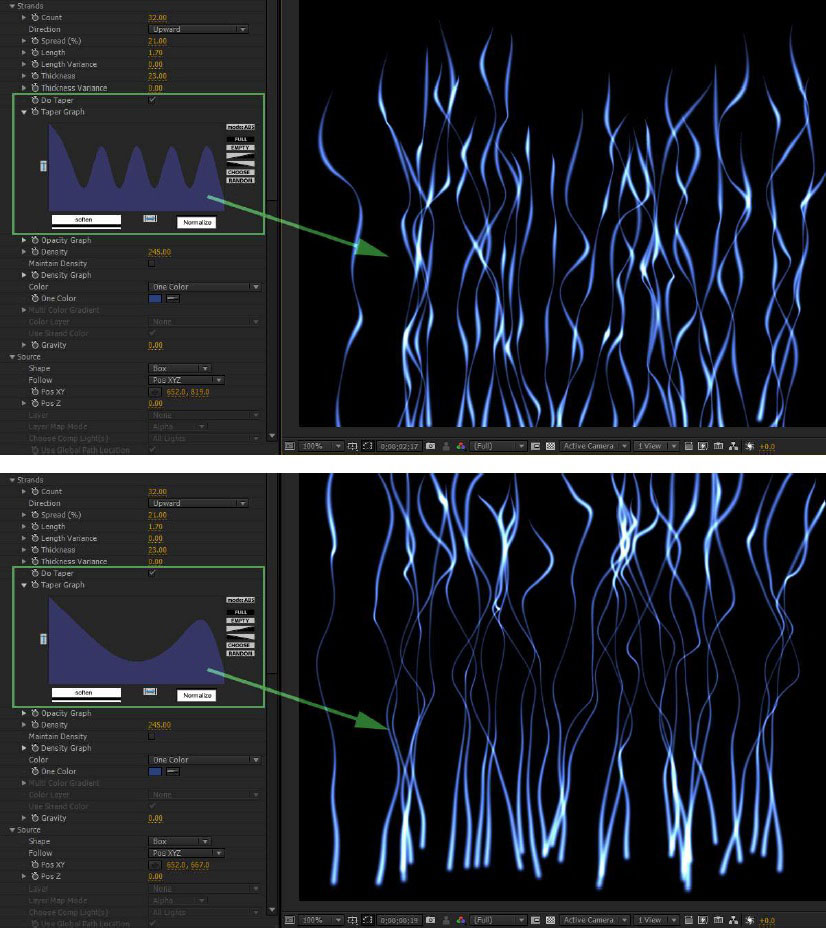
Taper and Taper Graph ; allow for varying the thickness along the strands. The left edge of the graph represents the beginning of the strand (nearest the source) and the right edge the far end of the strand 9away from the source).
Opacity Graph ; offers the same function as the taper graph, except for Opacity rather than thickness
Density, Maintain Density, Density Graph ; Density determines the density of particles making up the strand. Maintain Density attempts to maintain more uniform density when the strands are being stretched by the Organic Noise pattern. Density Graph (enabled only when Maintain Density is disabled) is like the Taper or Opacity graphs except that it applies to the density of particles along the strands.
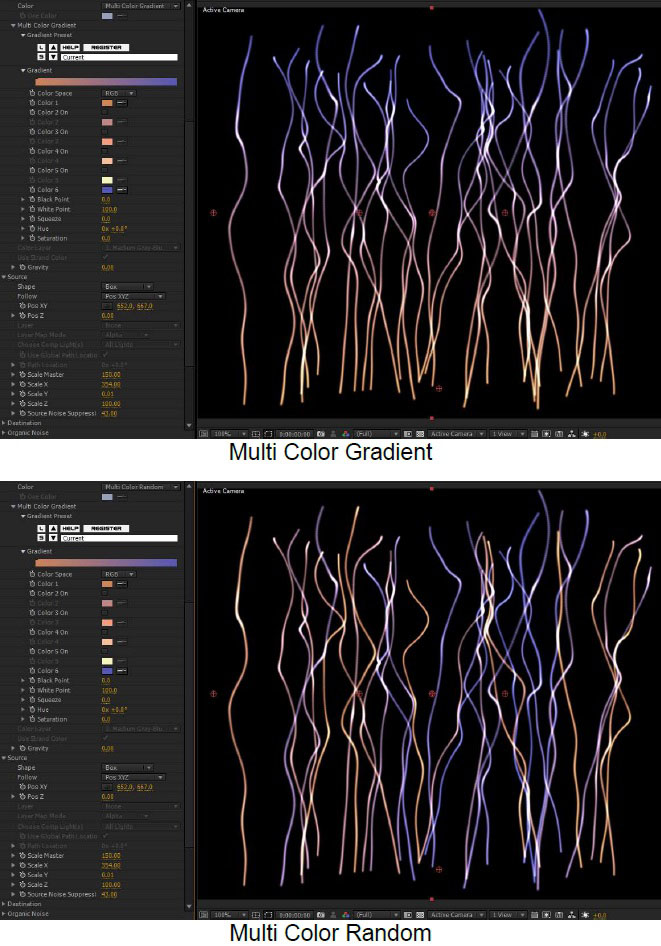
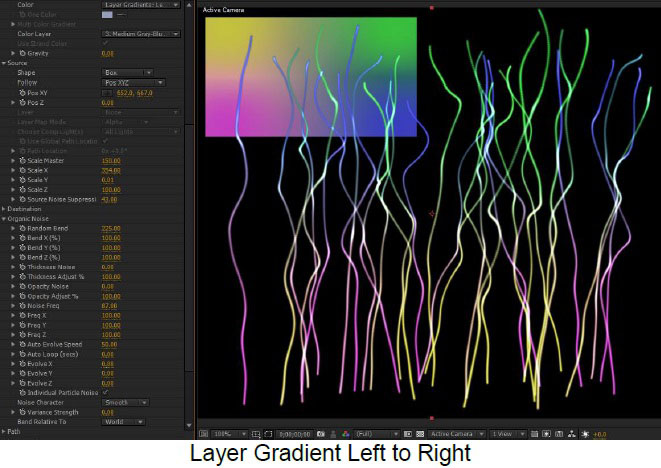
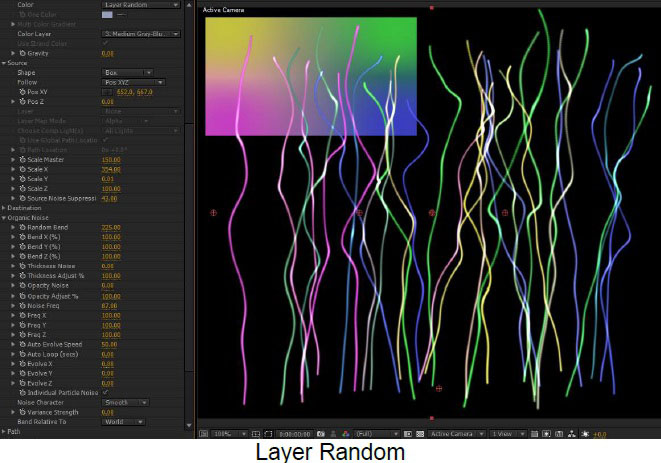
Color, Multicolor Gradient, and Color Layer ; The Color popup menu enables a variety of options for determining the color of the strands, based on a single color, a gradient generated within the plugin, or an alternate layer in the AE composition.
Gradient
The BCC Gradient group enables complex, multi-color gradients for use in a variety of effect settings such as colorizing light sources.
For more information on the BCC Gradient tool, Click Here.
Gravity will pull the strands down (positive Gravity number) or up (negative number) behaving as if the strands are attached to the source shape.
Source
Shape ; the source Shape can be a Point, Sphere, Box, or an AE layer.
Follow; the Follow popup menu offers options for having the Source follow an AE 3D layer or AE Mask or the Pos XYZ parameters
Layer and Layer Map Mode ; when using a Shape of Layer Map or the Follow 3D Layer option, the Layer popup is where the layer is selected. Layer Mode of Alpha or Luma refers to the Layer Map feature ; For Layer Map, strands will come off the source where there are white (Luma) or opaque (Alpha) pixels. For the Follow 3D Layer feature to work, the selected AE layer must be a 3D layer
Scale Master, Scale X, Y, and Z ; Scale adjustments for the source shape (does not scale the strands themselves or the particles making up the strands)
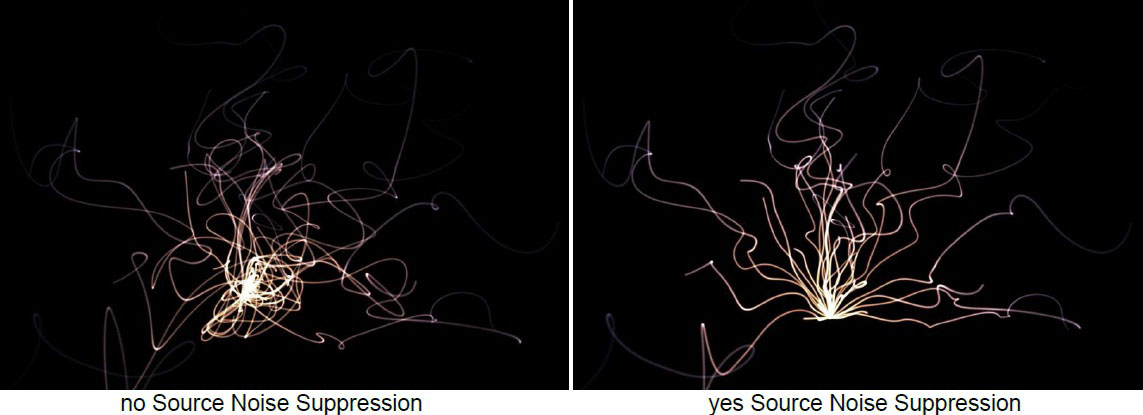
Source Noise Suppression ; allows for suppressing the effects of the Organic Noise on the source end of the strands
Destination
Use Destination Point ; when enabled a point in 3D space is defined as the destination point for the strands
Strength and Pull ; allow for adjusting / animating the effects of the destination point on the strands
Destination Noise Suppression ; allows for suppressing the effects of the Organic Noise on the destination end of the strands
Organic Noise
Random Bend, Bend X, Y, and Z ; determines the Amplitude of the Noise pattern that bends the strands
Thickness Noise and Opacity Noise; allow for applying the organic noise patter to the thickness and opacity along the strands
Noise Frequency, Frequency X, Y, and Z ; determines the frequency of the noise pattern with separate control for each axis
Auto Evolve Speed ; speed of the auto animation of the noise pattern – set to zero to turn off auto animation
Auto Loop ; the number of seconds at which the noise pattern animation will seemlessly loop
Evolve X, Y, and Z ; offsets for the noise pattern animation – can be used to manually animate noise
Individual Particle Noise ; when enabled, each card uses its own noise pattern rather than sharing a noise pattern, which results in an appearance that looks less like waves and more random.
Noise Character ; offers a variety of kinds of noise patterns
Movement
Move Progress ; can be used to move the strand in relation to the source (along the strand direction)
Move Random % ; can offset the movement between strands
Loop at Distance ; number of strand lengths at which the movement will loop back to the source
Auto Move and Move Speed ; allow for applying auto-animation to the Move Progress
Transform
Global Scale ; scale the overall strands effect including scale of the individual strands and particles
Center X, Y , and Z ; the 3D position of the strand effect
Rotate X, Y, Z ; strand effect rotation on 3 axes
Particles
Images – determines the source for the particles that are used to make up the strands. The options are the default Blurs, an image from the Image Collection (a customizable set of still graphics installed on the hard drive), or a Host Image Layer (an alternate layer from the comp)
Image Layer and Layer Mode ; when using a Host Layer image, these parameters allow you to select the layer and to determine which aspects of the image are used in the particles that make up the strands.
Blurriness ; determines the softness of the Blurs when using that image type.
Opacity: Sets the opacity of the particles in the strands.
Transfer Mode and Transfer Composite Mix ; determines the transfer mode used to composite between the particles and strands and allows for mixing the result back to Normal transfer mode.
Rotation, Bi-Directional Rotation, Rotation Random ; options for rotating the particles / strands (effects not noticeable when using round particles such as Blurs).
Effects
Mirror Mode ; options for mirroring strand effect to create symmetrical patterns
Disperse Master, Disperse X, Y , and Z ; disperses the particles from their original locations based on a random algorithm – a master control and control for dispersion along the individual 3D axes
Disperse Variance ; allows for adjusting the range of random dispersion between the particles
View Sphere Warpers ; the sphere warpers are 2 spherical fields that can attract or repel the particles that make up the strands
- SW Strength ; strength of the attraction (negative values) or repulsion force (positive values)
- SW Pos XYZ ; 3D position of sphere warper
- SW Radius ; size of the sphere warper
- SW Feather; allows for the influence of the sphere warper to be stronger toward the center of the spherical field
Built-in Camera
Camera Model ; Position, Orbit – camera offering 3D position and orientation control, or an orbit camera for easily adjusting perspective while remaining focused on the 3D center
Field of View ; an adjustment that can be used to simulate the look of various lenses – a large value gives a wide angle look
Camera Position X, Y, and Z ; 3D coordinate control for camera
Camera Tumble, Spin, and Rotate ; controls for orientation of the position based camera
Use Depth of Field, DOF Focal Point, Aperture, Blur ; controls for simulating camera depth of field
Global Settings
Random Seed ; there are several features in the plugin that use some kind of randomization to generate results (Organic Noise, Length and Thickness Variance, etc.). Changing the Random Seed tweaks the random algorithms to produce a somewhat different result. It can be used to simply try a few different takes on an effect and it can also be used when you want another instance of the effect to look the same but not identical give it a different Random Seed value.
Near and Far Clip Plane Adjust ; it is possible to trim or extend the range in which particles will appear in the effect. In most cases there is no need to adjust these parameters, but if you find a particle very near or far from the camera unexpectedly disappearing it is possible to use these parameters to correct it.
Alpha Cutoff %: Determines what alpha value is equivalent to zero for the particle renderer.
Z Sorting Mode ; Defaults to true 3D, with options for sorting by birth order.
Accessing Image Layers; Determines whether (and how) an animated Image Layer used as a particle will loop when the end is reached.
Beat Reactor
The BCC Beat Reactor is an animation control suite which drives effect properties based on the contents of an audio track. This lets you seamlessly tie visual FX to an audio soundtrack without the need for ANY manual keyframing.
Note that the Beat Reactor propagation options in do not generate the expected result in Organic Strands, and we recommend using non-propagation modes instead in this particular effect.
For more information on the Beat Reactor, Click Here.