 |
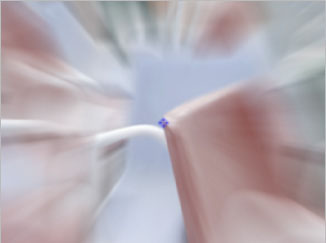 |
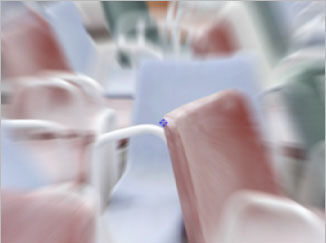
| Original Image | Filtered Image |
Overview
The BCC Radial Blur filter creates a blur around a specific point, simulating the affect of a zooming or rotating camera. The Amount option specifies the amount of blur, depending on the selection for Type. For a Spin blur, which applies blurs in circles around the center point, the Amount value indicates the degree of rotation. For a Zoom blur, which applies blur that radiates out from the center point, the Amount value specifies the degree of radial blurring.
Function
Presets and Common Controls
BCC filters come with a library of factory installed presets plus the ability to create your own custom presets and preview them with the BCC FX Browser™.
BCC filters also include common controls that configure global effect preferences and other host-specific effect settings.
For more information about working with presets and other common controls, Click Here.
Compare Mode
The BCC Compare Mode provides a convenient mechanism to compare the effect result with the original source layer. It provides several variations on basic split-screen views with the filtered clip placed next to the unedited original.
For more information on the Compare Mode, Click Here.
Compare Mode pop-up: Controls what is displayed by the Compare Mode. The options are:
- Off shows the output of the filter.
- Side By Side the left side of the output shows half of the incoming image, and the right side shows the same half of the image as processed by the filter. When in Side-by-Side mode, the corresponding Slide and Right Offset sliders become available.Wipe enables the user to interactively wipe the effect across the image. The left side of the wipe bar on the image output shows the unfiltered image, while the right side of the wipe bar shows the filtered result. When in Wipe mode, the corresponding Wipe slider becomes available.
- Wipe/Slide operates as a Wipe function when Wipe is selected in Compare Mode, and as a Slide function when Side-‐By-‐Side is selected in Compare Mode. When in Wipe mode, adjustments to this parameter moves the vertical wipe bar across the image; the region on the left of the wipe bar shows the original unfiltered image, while the region on the right shows the filtered result. When in Slide mode, adjustments to this parameter pans the image in the viewer window, maintaining the spatial relationship in the viewer between the before and after images.
- Right Offset provides a way to adjust the spatial relationship between the unfiltered original image and the filtered result in the viewer window. Adjustments to this parameter will offset the position of the filtered image in the viewer.
The Blur Type menu sets the type of motion blur that is created. The choices are Blur or Smear. Smear blurs the pixels in one direction. Blur blurs the pixels symmetrically.
Center sets the coordinates of the center of the radial blur.
 |
 |
| Center X=360, Center Y=243 | Center X=775, Center Y=100 |
Blur Amount sets the amount of blur or smear that is applied to any moving pixels in the image. Positive values apply the blur or smear; negative values sharpen these pixels. The following example uses a Smear Blur Type.
 |
 |
 |
| Blur Amount= -50 | Blur Amount=25 | Blur Amount=75 |
When the Blur Type menu is set to Smear, Smear Falloff determines the falloff. Falloff is the transition between the smeared and unsmeared areas. At a value of 0, the Smear is fully applied; at a value of 100, the smear has no affect on the image. This is ideal for animating the smear. Smear Falloff is dimmed unless Smear is chosen as the Blur Type.
 |
 |
| Smear Falloff=5 | Smear Falloff=75 |
Blur Threshold reduces the amount of color changes to each pixel by the threshold amount. Increasing Blur Threshold causes the parts of the image with abrupt changes in color to blur, while areas with subtle details remain unchanged.
Maximum Deviation sets the maximum deviation (based on 8-bit color) allowed for any channel. Reducing this value limits the amount any color can change. This control becomes more noticeable at values below 30. Very small amounts of Max. Deviation can be useful (especially combines with the PixelChooser) to reduce noise in video and digital stills that contain noise in their dark areas.
The Apply Mode menu controls how the filtered image is composited with the source image. For descriptions of all the possible Apply Modes, Click Here.
Apply Mix controls the mix of the specified Apply Mode with the Normal apply mode. If the Apply Mode is Normal, Apply Mix has no affect and the parameter does not appear. If Apply Mix is 0, Apply Mode has no affect. Increase Apply Mix to blend the Apply Mode setting with the Normal apply mode.
Mix with Original blends the source and filtered images. Use this parameter to animate the effect from the unfiltered to the filtered image without adjusting other settings, or to reduce the affect of the filter by mixing it with the source image.
Motion Tracker
The BCC Motion Tracker allows you to track the motion of an object, then use the motion path to drive other geometric properties of the effect without the need for keyframing.
For more information on the Motion Tracker, Click Here.
If you are using the controls in the PixelChooser parameter group, the Apply PixelChooser menu determines when the PixelChooser controls are applied to the blurred image.
- Choose Post-Effect for the PixelChooser to affect the image before the blur is applied.
- Choose Pre-Effect for the PixelChooser to affect the image after the blur is applied.
- Choose Both for the PixelChooser to affect the image both before and after the blur is applied.
PixelChooser
The BCC PixelChooser provides simple, built-in masking of the effect result. The PixelChooser is generally used to select a portion of the image and restrict an effect to just the selected area while maintaining the original image content in unselected regions. The selection can be based on geometric shapes or on the image’s luma/color properties.
For more information on the PixelChooser, Click Here.
Beat Reactor
The BCC Beat Reactor is an animation control suite which drives effect properties based on the contents of an audio track. This lets you seamlessly tie visual FX to an audio soundtrack without the need for ANY manual keyframing.
For more information on the Beat Reactor, Click Here.