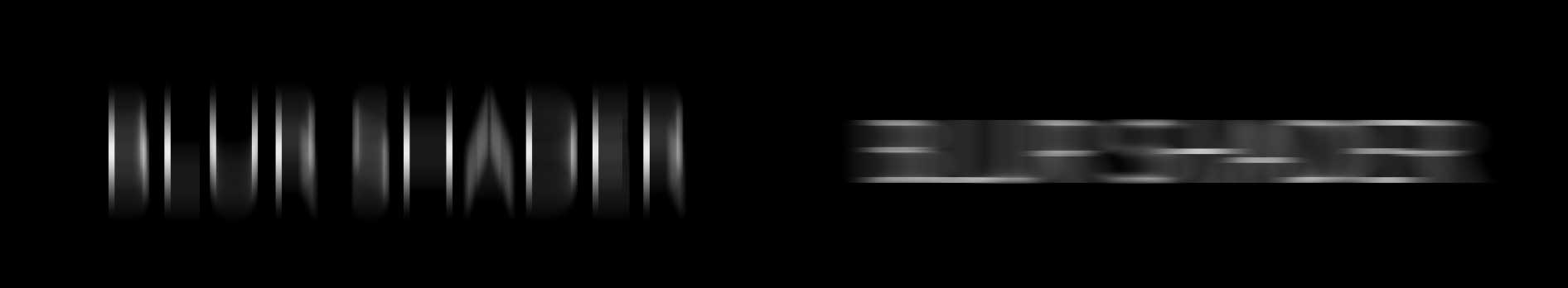Blur
In this section we will cover the available blur IP Shaders that are available in Title Studio with Continuum 2019. There are five types of blur that can be applied to an object, material or scene in Title Studio:
- Blur
- Directional Blur
- Prism Blur
- Radial Blur
- Spiral Blur
The blur style can be selected from the Type drop down menu. Once selected, the Material Attributes window will update to reflect the parameters specific to the selected blur style.
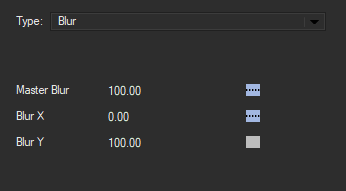
Blur emulates the look of shooting in soft forcus or with lens difusion. This image processor allows you to blur the individual horizontal and vertical components of of the image.
Master Blur controls the overal level of blur present. Higher values will produce softer results, while a value of zero will produce no blur at all

Master Blur Values set to 0, 25 and 100 respectively. The higher the value, the softer the image will become.
Blur X and Blur Y control the overall level of blur along the x and y axis respectively. Higher values will produce softer results.
The Blur X and Y parameters are directly tied to the Master Blur controls. So, for example, a Master Blur value of zero will produce no blur regardless of what the value of the X or Y parameters are.
However, if the Master Blur is set to 100 and the Blur X is set to zero, the resulting blur will be stretched along the Y axis.
Directional Blur emulates the look of soft directional blurs to simulate the appearance of motion.
As before, the Master Blur controls the overal level of blur present. Higher values will produce softer results, while a value of zero will produce no blur at all.
The Rotate parameter allows you to select the direction of the motion and can be keyframed for some interesting results. By default it is set to 90 degrees, which simulates the appearance that the object is moving left to right along the X axis. Adjustments to the angle value will change the direction of your blur.
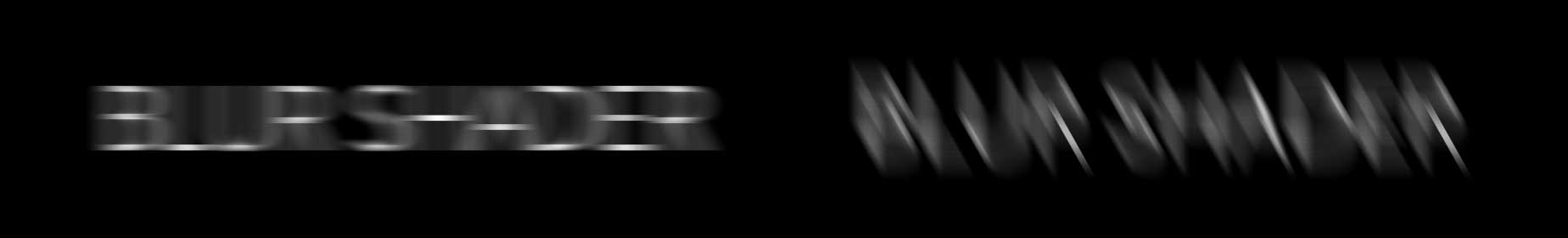
Here, the Rotate Angle is set to 90 degrees and 150 degrees respectively. Adjustments to this value, change the direction of the blur.
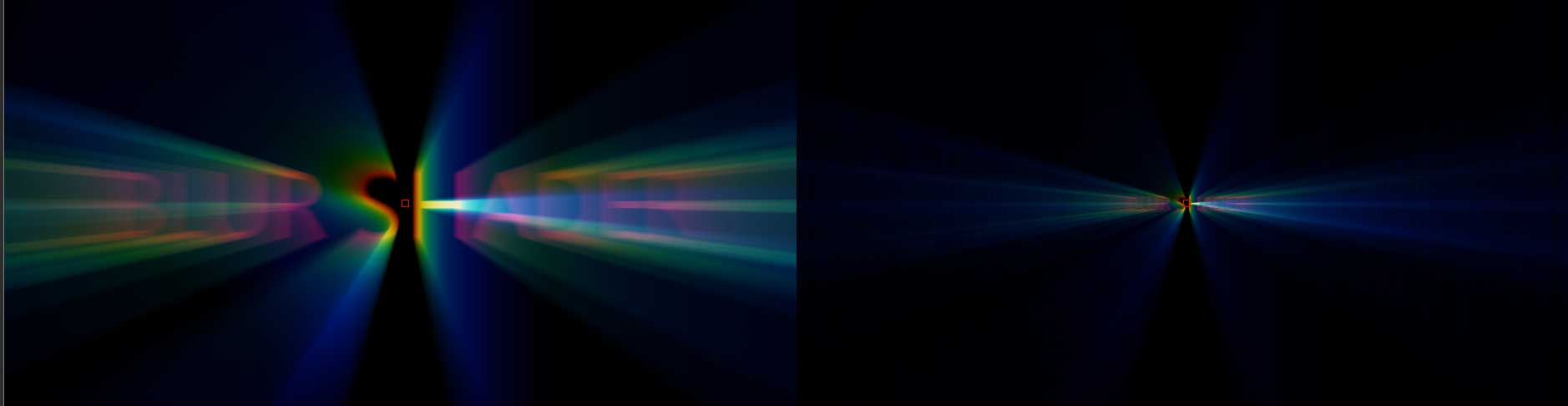
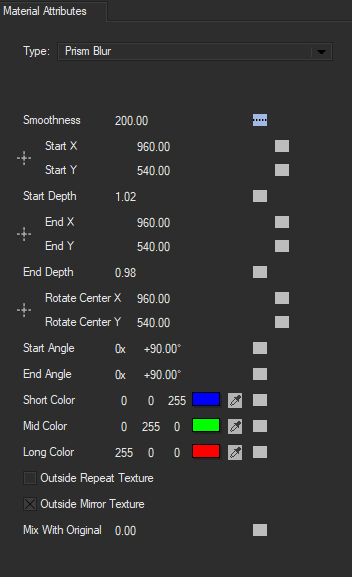
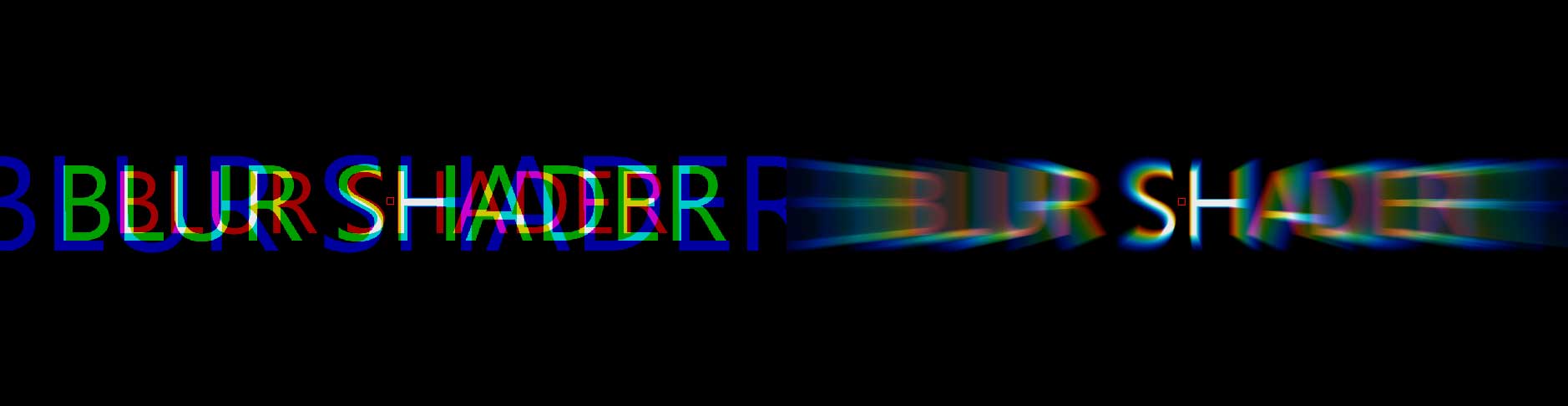
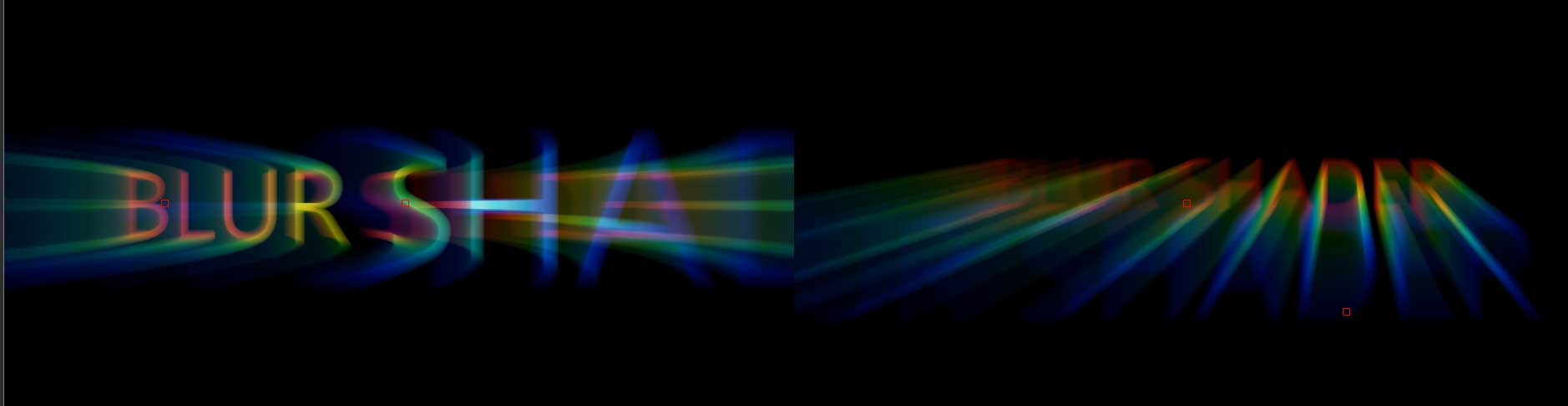
Prism Blur: simulates the photographic effect of chromatic aberration, where a bad lens can create prismatic color fringing along edges of contrast within the image.
unlike with other blur types, Prism Blur does not have a Master Blur setting. Instead, it features parameters designed to increase the depth of the chromatic aberration.
Smoothness controls the number of samples present. Lower values produce fewer samples, while higher values produce smoother reslts.
Start Depth and End Depth control the depth of the first and last sample. Higher vales will bring the blur closer to the camera, while lower values move it further from the camera. By keyframing these values, it is possible to recreate title effects similar to the opening credits of the 1978 Superman movie.
Each depth control also features parameter for Start/End X and Start/End X. By defalt, the blur is centered in the middle of the frame, however, by adujsting these values, you can easily change the direction of the blur along the x and y axis.
Similar to the Start/End X and Start/End Y, Rotate Center X and Rotate Center Y controls the rotation of the center point, allowing for additional rotation to the blur.
Short, Mid and Long Color values control the color of the blur. Colors can easily be changed by selecting the color chip or eye dropper.
Outside Repeat Texture tiles the blur texture along the outside edge to create a smoother and seamless blur
Outside Mirror Texture mirrors the blur texture to reflect the effect along the outside edges.
Mix With Original: Blends the effect back with the original unfiltered clip.
Radial Blur creates a blur around a specific point, simulating the affect of a zooming or rotating camera.
As with other types of blurs, the Master Blur controls the intesity and depth of the blur. Higher vales will produce more zoomed out and smoother results.
Center X and Center Y parameters allow for the adjstment of the center point of the blur.
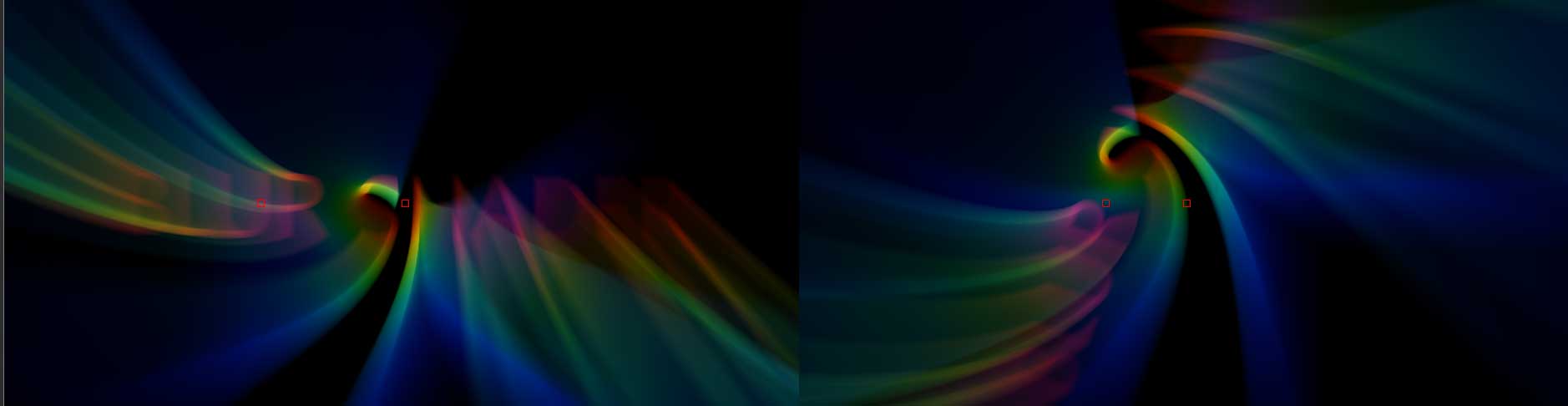
Spiral Blur creates a blur or smear that appears as though it is spiraling toward the center of the image.
The Rotate parameter determines the degree to which the blur spirals outward. Higher values will produce more drastic fanning of the object.
Zoom Blur acts similar to a Radial Blur in that it simulates a zoom in the blur. Higher values will produce more drastic zooms.
Smear creates a more distorted and smeared effect.